When it comes to Search Engine Optimization (SEO), the choice between long-tail vs short-tail keywords can significantly impact your strategy’s effectiveness. These keywords represent two different approaches to optimizing your website for search engines. Each comes with its own set of advantages and drawbacks, making it essential to understand their differences and how you should apply them to your topic.
What’s the difference between long-tail vs short-tail keywords, you might wonder? Why should you consider a long-tail keyword strategy, especially if you’re new in the online world?
Before we explore the differences between these 2 types of SEO keywords and see some examples, let’s get familiar with some definitions.
What is a Short and what is a Long-tail Keyword?
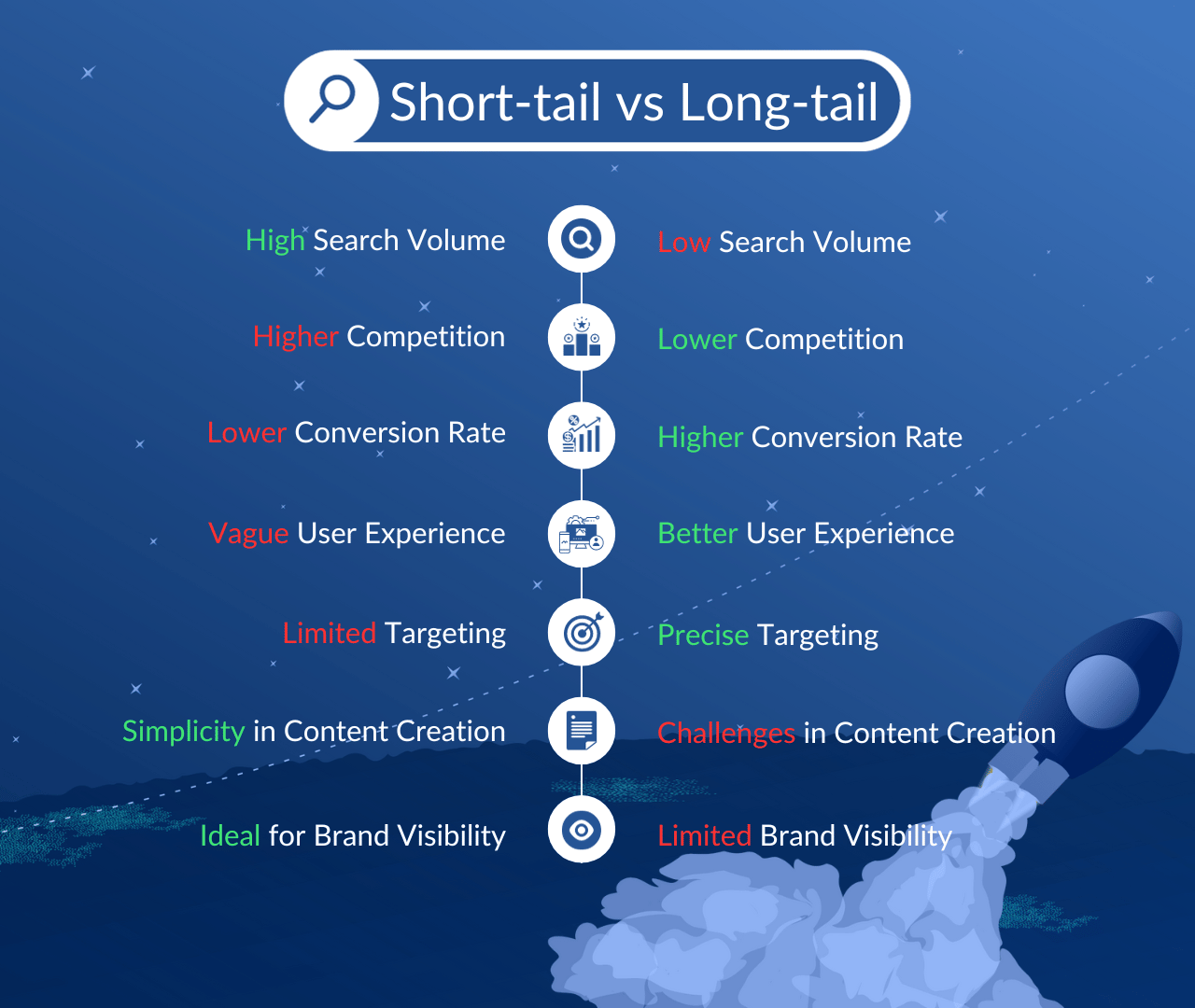
A short-tail keyword, often referred to as a “broad keyword,” is a brief and general word phrase typically consisting of one to three words. Short-tail keywords are broad in scope and do not provide much context about the user’s intent. They are often highly competitive because many websites aim to rank for these general terms.
Examples include “shoes,” “travel,” or “digital marketing.”
Whereas…
Long-tail keywords are longer and more specific word phrases that typically consist of three or more words. These keywords are more detailed and provide a clearer understanding of the user’s intent. Long-tail keywords are often less competitive than short-tail keywords and are used to target niche audiences or address specific search queries.
Examples of such keywords include “red running shoes for women,” “best budget travel destinations in Europe,” or “digital marketing strategies for small businesses.”
The Battle (Pros and Cons)
Let’s take a closer look at the benefits and drawbacks of each keyword type.
-
-
Short-tail Keywords
-
(+) High Search Volume: They potentially bring more traffic to your website due to higher search volumes.
(+) Broad Reach: They target a broad audience, making them suitable for brand visibility and general awareness.
(+) Simplicity: Short keywords are concise and straightforward, making them easy to integrate into content.
(+) Competitive Advantage: Ranking for short-tail keywords can provide a competitive advantage in the industry.
(+) Niche Domination: In some cases, a well-optimized keyword can help establish your authority in a niche.
(-) High Competition: They usually have high competition, making it challenging to achieve top rankings.
(-) Insufficient User Intent: Users searching with that type of term may have diverse intents, making it harder to provide precisely what they’re looking for.
(-) Lower Conversion Rates: Visitors may be in the early stages of their buying journey, resulting in lower conversion rates.
(-) Limited Targeting: Short keywords may not effectively reach specific or niche audiences.
-
-
Long-tail Keywords
-
(+) Lower Competition: Long-tail keywords typically have lower competition, making it easier to achieve high rankings.
(+) Higher Conversion Rates: Users searching with that type of word often have specific needs or intent, leading to higher conversion rates.
(+) Precise Targeting: They enable you to target specific niches or user segments.
(+) Better User Experience: By addressing specific user queries, you can provide highly relevant content, improving, as a result, the user experience.
(+) Voice Search Optimization: Long-tail keywords align with the conversational nature of voice search, which is growing in popularity.
(-) Lower Search Volume: They generally have lower search volumes, which may limit traffic potential.
(-) Content Creation Challenges: Developing content for numerous long-tail keywords can be time-consuming.
(-) Constantly Evolving: As for the trends, they can change more rapidly due to evolving user queries.
(-) Tracking and Management: Managing a large number of keywords can be complex and require effective tracking.
(-) Limited Brand Visibility: Relying solely on long terms may limit your brand’s visibility for broader, generic search queries.
A well-balanced SEO strategy often involves a combination of both SEO keyword types. The former can help with broad visibility, while the latter is valuable for targeting specific, high-conversion intent. The choice depends on your specific SEO goals and the competitive landscape of your industry.
Long-tail vs Short-tail Keywords Examples
We have already mentioned the structure of each type and how you can distinguish a short from a long keyphrase. 1-3 words are typically a short form of a keyphrase, whereas 3+ words are desirable for a long-tail term.
-
Example 1: “Running Shoes”
“Running shoes” is a broad term, while “Running shoes for men with high arch support” is a good long-tail keyword example.
-
Example 2: “Budget Travel Destinations”
“Budget Travel Destinations” makes unclear what the user is looking for, whereas the term “Budget travel destinations in Southeast Asia” is more specific.
-
Example 3: “Digital Marketing Strategies”
The term “Digital marketing strategies” consists of a short-tail keyword in contrast to “The best digital marketing strategies for e-commerce businesses” which specifies what the user is searching for.
-
Example 4: “Fitness”
In this example, the word “fitness” is extremely broad resulting in great search volume activity as well as high competition. On the other hand, “High-intensity interval training workouts for weight loss” could be an opportunity for a small website to rank in SERPs.
-
Example 5: “Used Cars California”
“Used Cars California” is definitely a broader term than“Used hybrid cars under $10,000 in California” which indicates what the user is searching for.
How to Find Long-tail Keywords
Discovering keyphrases with lower competition can be challenging. However, there are paid and free methods to follow and find profitable words. Assuming you have understood your target audience and what are the real needs in your niche industry, you can unveil precious data in the following ways:
-
-
Utilize Keyword Research Tools
-
Employ tools such as Google Keyword Planner [free], SEMrush [paid], Ahrefs [paid], Moz Keyword Explorer [paid], or Ubersuggest [paid] to generate keyword ideas. Enter your seed (short-tail) keywords into these tools to uncover related long-tail keyword suggestions.
-
-
Check Google’s Autocomplete and Related Searches
-
Use search engines like Google. Start typing your seed keywords into the search bar and note the autocomplete suggestions that appear. Also, scroll to the bottom of the search results page to find related search queries.
-
-
Explore User-Generated Content
-
Forums, social media platforms, and community websites are places where people discuss topics related to your niche. User-generated content can provide insights into the specific phrases and questions your audience is using.
-
-
Review Site Analytics
-
If you already have a website, analyze your site’s analytics data to identify the search queries that are driving traffic to your site. These queries may include valuable terms.